India and Israel have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) on industrial research and development cooperation, marking a significant milestone in their scientific and technological partnership
Key Points On India and Israel relations
- The agreement was signed between the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) under the Ministry of Science and Technology of India, and the Directorate of Defence Research and Development (DDR&D) under the Ministry of Defence of Israel.
- The collaboration aims to enable joint industrial research and development projects in various high-tech fields such as artificial intelligence, quantum and semiconductors, synthetic biology, healthcare, aerospace, sustainable energy, and agriculture, among others.
- The MoU will be implemented through specific projects agreed upon by both parties and monitored by a Joint Steering Committee led by the heads of CSIR and DDR&D.
- The event also highlighted the successful diplomatic relations between the two countries, which have strengthened into a strategic partnership.
India and Israel History
- Relations between Israel and India have not always been as friendly as they are today.
- India remained invested in the idea of Arab freedom in Palestine in the lead up to its independence in August 1947 and thereafter.
- It was an elected member of the UN Special Committee on Palestine (UNSCOP). And, in September 1947, it was one of only 13 countries that voted against the United Nations’ Partition Plan for Palestine.
- In 1974, it became the first non-Arab country to recognise the Palestinian Liberation Organization (PLO) as the sole, legitimate representative of the Palestinian people.
- In 1975, the government of India also allowed the PLO to open an office in New Delhi as confirmation of its continued support to the Palestinian “struggle for the restoration of their inalienable rights in their homeland”.
- India recognised the State of Palestine in 1988 and it opened the doors of its first representative office in Palestine in 1996.
- However, with the fall of the Soviet Union, India engaged in a process of economic liberalisation and, with it, began to reposition itself in world politics. This included its relationship with Israel.
- India officially recognized Israel in 1950, both countries established full diplomatic ties only on 29th January 1992.
- In 1992, under the leadership of Prime Minister PV Narasimha Rao, India established formal diplomatic ties with Israel, but remained committed to the Palestinian cause and its economically crucial ties with other countries in the Middle East.
India And Israel Political Relations
- India announced its recognition of Israel on September 17, 1950.
- Soon thereafter, the Jewish Agency established an immigration office in Bombay.
- This was later converted into a Trade Office and subsequently a Consulate. Embassies were opened in 1992 when full diplomatic relations were established.
- Since the upgradation of relations in 1992, defence and agriculture formed the two main pillars of bilateral engagement.
- Prime Minister Modi undertook an historic first ever visit by an Indian PM to Israel in 2017
India And Israel Economic Cooperation
- Trade between India and Israel has increased from USD 5 billion before the Covid-19 pandemic to about USD 7.5 billion till 2023 January.
- Trade in diamonds constitutes about 50% of bilateral trade.
- India is Israel’s third-largest trade partner in Asia and seventh largest globally.
- Israeli companies have invested in India in energy, renewable energy, telecom, real estate, water technologies, and are focusing on setting up R&D centers or production units in India.
- India is also in dialogue with Israel for concluding a Free Trade Agreement (FTA).
India And Israel Agriculture
- Under a comprehensive Work Plan for cooperation in agriculture signed on 10 May 2006, bilateral projects are implemented through MASHAV (Center for International Cooperation of Israel’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs) and CINADCO (Centre for International Agricultural Development Cooperation of Israel’s Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development).
- Agricultural cooperation between the two sides is formalized through 3-year Work plans wherein 3-year Action plans are developed.
- India has benefited from Israeli expertise and technologies in horticulture mechanization, protected cultivation, orchard and canopy management, nursery management, micro- irrigation and post-harvest management
- Israeli drip irrigation technologies and products are now widely used in India
- Some Israeli companies and experts are providing expertise to manage and improve dairy farming in India through their expertise in high milk yield.
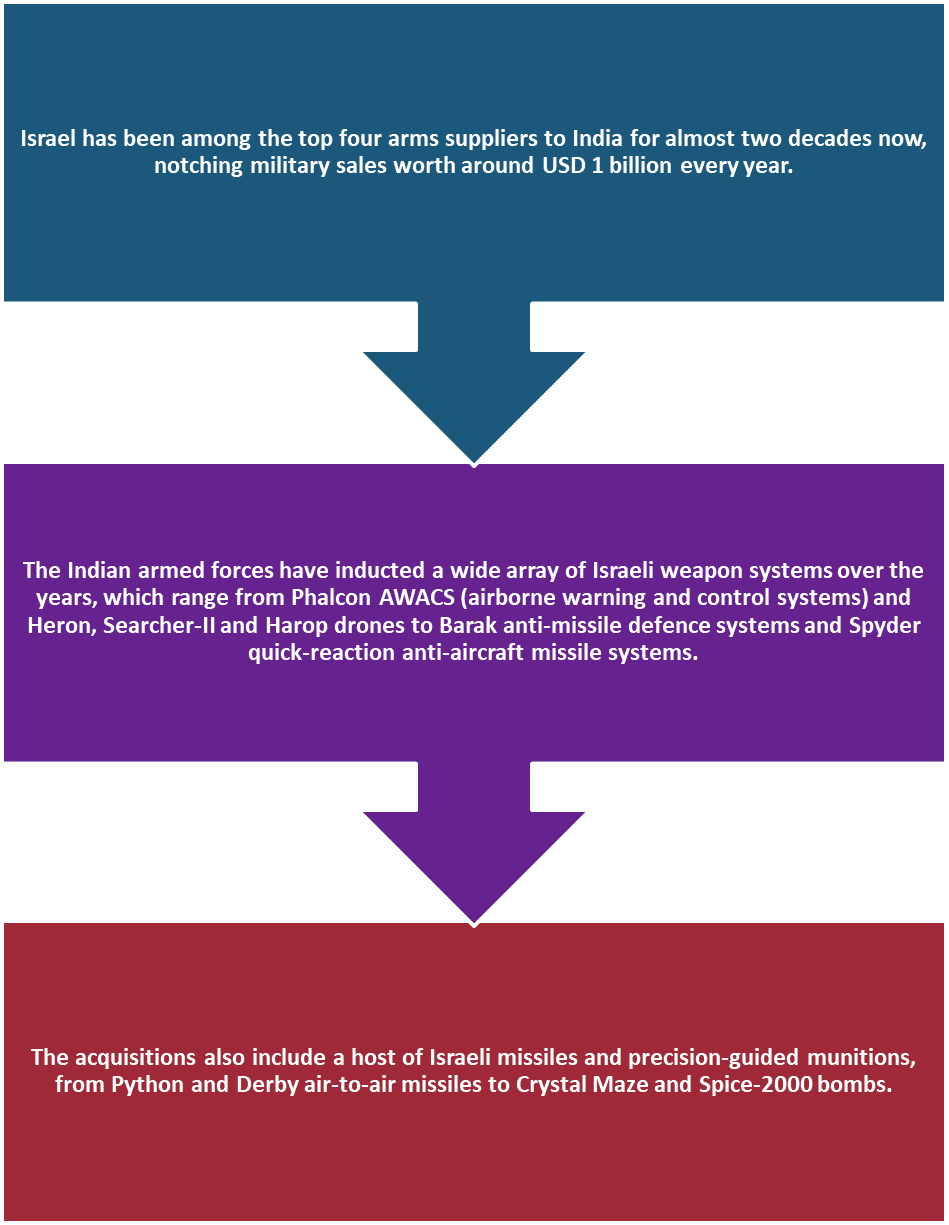
India And Israel Defence Cooperation
To Download Monthly Current Affairs PDF Click here
Get Inspiration from CLAT 2025 Topper
Click here to get a free demo
Everything About CLAT 2025



