Union Minister of Commerce and Industry, Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution and Textiles, Shri Piyush Goyal launched the Foreign Trade Policy 2023-2028
Key Points On Foreign Trade Policy
- India’s overall exports, including services and merchandise exports, has already crossed US$ 750 Billion and is expected to cross US$ 760 Billion this year, he said.
- Foreign Trade Policy (2023) is a policy document which is based on continuity of time-tested schemes facilitating exports as well as a document which is nimble and responsive to the requirements of trade.
- The FTP 2023 aims at process re-engineering and automation to facilitate ease of doing business for exporters.
- The government aims to increase India’s overall exports to USD 2 trillion by 2030, with equal contributions from the merchandise and services sectors.
- The term of the previous five year policy had ended in March 2020. However, it has been extended repeatedly in wake of Covid outbreak and resulting lockdowns.
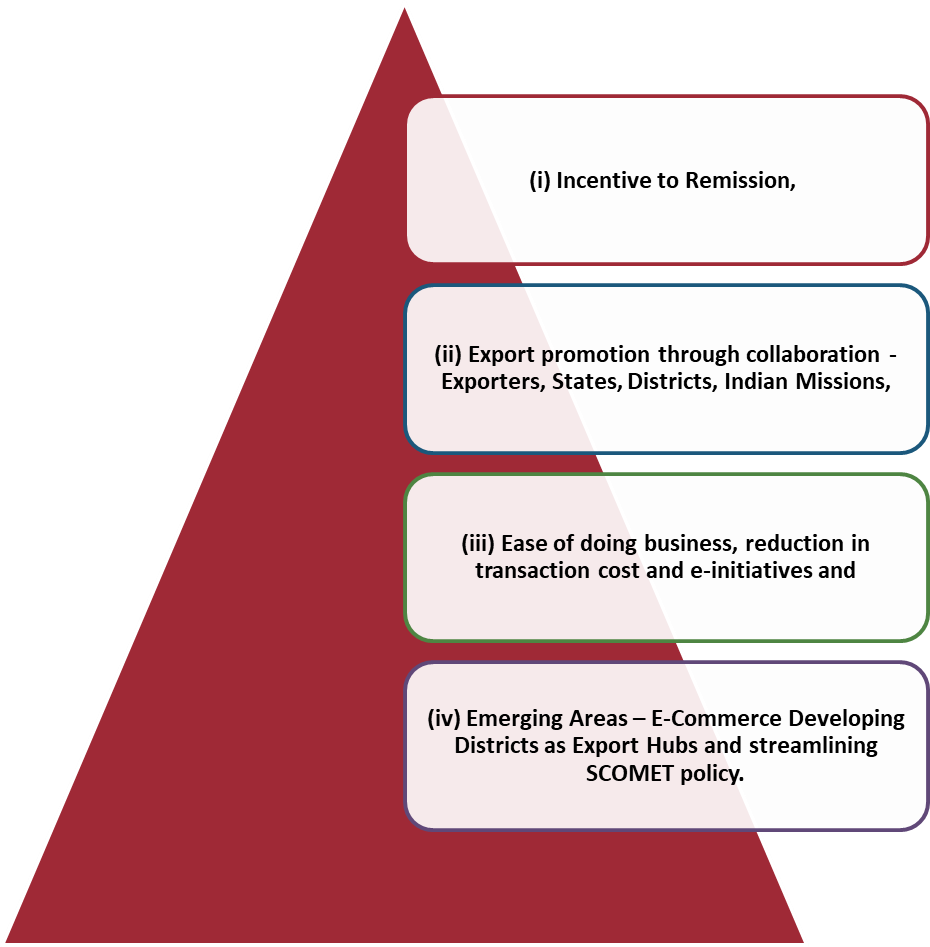
Pillars Of Foreign Trade Policy
The Key Approach to the policy is based on these 4 pillars:
Features Of Foreign Trade Policy
Process Re-Engineering and Automation
- The policy emphasizes on technology interface and principles of collaboration regime
- This will make it easier for MSMEs and others to access export benefits.
- Duty exemption schemes for export production will now be implemented through Regional Offices in a rule-based IT system environment, eliminating the need for manual interface
Towns of Export Excellence
- Four new towns, namely Faridabad, Mirzapur, Moradabad, and Varanasi, have been designated as Towns of Export Excellence (TEE) in addition to the existing 39 towns.
- The TEEs will have priority access to export promotion funds under the MAI scheme
- This addition is expected to boost the exports of handlooms, handicrafts, and carpets.
Recognition of Exporters
- Exporter firms recognized with ‘status’ based on export performance will now be partners in capacity-building initiatives on a best-endeavor basis.
- Similar to the ‘each one teach one’ initiative, 2-star and above status holders would be encouraged to provide trade-related training based on a model curriculum to interested individuals.
Promoting export from the districts
- The FTP aims at building partnerships with State governments and taking forward the Districts as Export Hubs (DEH) initiative to promote exports at the district level and accelerate the development of grassroots trade ecosystem.
Streamlining SCOMET Policy
- India is placing more emphasis on the “export control” regime to comply with the international treaties and agreements entered into by India.
- There is a wider outreach and understanding of SCOMET (Special Chemicals, Organisms, Materials, Equipment and Technologies) among stakeholders, and the policy regime is being made more robust to implement international treaties and agreements entered into by India.
- This would provide access of dual-use High end goods and technologies to Indian exporters while facilitating exports of controlled items/technologies under SCOMET from India.
Facilitating E-Commerce Exports
- Various estimates suggest e-commerce export potential in the range of USD 200 to USD 300 billion by 2030.
- FTP 2023 outlines the intent and roadmap for establishing e-commerce hubs and related elements such as payment reconciliation, book-keeping, returns policy, and export entitlements.
Facilitation under Export Promotion of Capital Goods (EPCG) Scheme
- The EPCG Scheme, which allows import of capital goods at zero Customs duty for export production, is being further rationalized.
- Prime Minister Mega Integrated Textile Region and Apparel Parks (PM MITRA) scheme has been added as an additional scheme eligible to claim benefits
- Dairy sector to be exempted from maintaining Average Export Obligation – to support dairy sector to upgrade the technology.
- Battery Electric Vehicles (BEV) of all types, Vertical Farming equipment, Wastewater Treatment and Recycling, Rainwater harvesting system and Rainwater Filters, and Green Hydrogen are added to Green Technology products – will now be eligible for reduced Export Obligation requirement under EPCG Scheme
Facilitation under Advance authorization Scheme
- AAS provides duty-free import of raw materials for manufacturing export items.
- It has been now extended to the export of the Apparel and Clothing sector
Merchanting trade
- Merchanting trade of restricted and prohibited items under export policy would now be possible.
- Merchanting trade involves shipment of goods from one foreign country to another foreign country without touching Indian ports, involving an Indian intermediary.
Amnesty Scheme
- The government is introducing a special one-time Amnesty Scheme under the FTP 2023 to address default on Export Obligations.
- This scheme is intended to provide relief to exporters who have been unable to meet their obligations under EPCG and Advance Authorizations, and who are burdened by high duty and interest costs associated with pending cases
To Download Monthly Current Affairs PDF Click here
Get Inspiration from CLAT 2025 Topper
Click here to get a free demo
Everything About CLAT 2025



