Egypt unveiled the discovery of long corridor inside the Great Pyramid of Giza, the first to be found on the structure’s north side.
The Great Pyramid of Giza Corridor
- The corridor, which measures 9 meters (nearly 30 feet) by 2 meters (more than 6 feet), is perched above the famous structure’s main entrance and was detected using a scan
- The function of the chamber is currently unknown, although such corridors often lead to further archaeological discoveries.
- The initial finding was made by the ScanPyramids project in 2016 using a non-invasive method called cosmic-ray muon radiography.
Cosmic-Ray Muon Radiography (CMR)
- The corridor has been unearthed by using a non-invasive technique called cosmic-ray muon radiography.
- CMR is a technique used to study the density and composition of materials hidden within large and dense objects, such as geological formations, archaeological sites, and industrial facilities.
- The technique involves using muons, a type of cosmic-ray particle, to generate images of the interior of such objects.
- Muon particles are created when cosmic rays, mostly protons and atomic nuclei, collide with atoms in the Earth’s upper atmosphere.
- These muons travel through the atmosphere and penetrate deep into the ground, passing through objects along their path.
- Muons are highly penetrating particles that can penetrate several meters of rock or other materials, making them ideal for imaging the internal structure of objects.
The Great Pyramid Of Giza
- The Great Pyramid was built as a monumental tomb around 2560 BC, during the reign of the Pharaoh Khufu, or Cheops.
- The Great Pyramid of Giza is the largest Egyptian pyramid and the tomb of Fourth Dynasty pharaoh Khufu, who is widely regarded as the greatest emperor of ancient Egypt.
- The pyramid is the oldest of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, and the only one to remain largely intact.
- The pyramid was constructed out of 2.5 million stone pieces that each weighed between 2.5 and 15 tonnes.
- It was the tallest structure on the planet until the main spire of the Lincoln Cathedral in the United Kingdom overtook it in 1400 AD
- It is located on the Giza plateau, five miles to the west of the Nile River ,near the city of Cairo, Egypt.
- It was built by Khufu (Cheops), the second king of Egypt’s 4th dynasty (c. 2575–c. 2465 BCE).
- Until the Eiffel Tower was completed in Paris, France, in 1889, the Great Pyramid was the tallest structure made by human hands in the world; a record it held for over 3,000 years.
- The pyramid was first excavated using modern techniques and scientific analysis in 1880 by Sir William Matthew Flinders Petrie (l.1853-1942), the British archaeologist.
Features Of The Great Pyramid Of Giza
- When the pyramid was built, it was around 481 feet tall. Today, because of erosion and the removal of the top piece, the pyramid is around 455 feet tall. At its base, each side is approximately 755 feet long.
- It is comprised of over two million blocks of stone. Each of the stone blocks is estimated to weigh over 2000 pounds (907 kg).
- Inside the Great Pyramid are three major rooms: the King’s Chamber, the Queen’s Chamber, and the Grand Gallery. Small tunnels and air shafts lead to the chambers from the outside.
- The pyramid’s sides rise at an angle of 51.87° and are accurately oriented to the four cardinal points of the compass.
- The Great Pyramid’s core is made of yellowish limestone blocks, and the inner passages are of finer, light-coloured limestone.
- The interior burial chamber is built of huge blocks of granite.
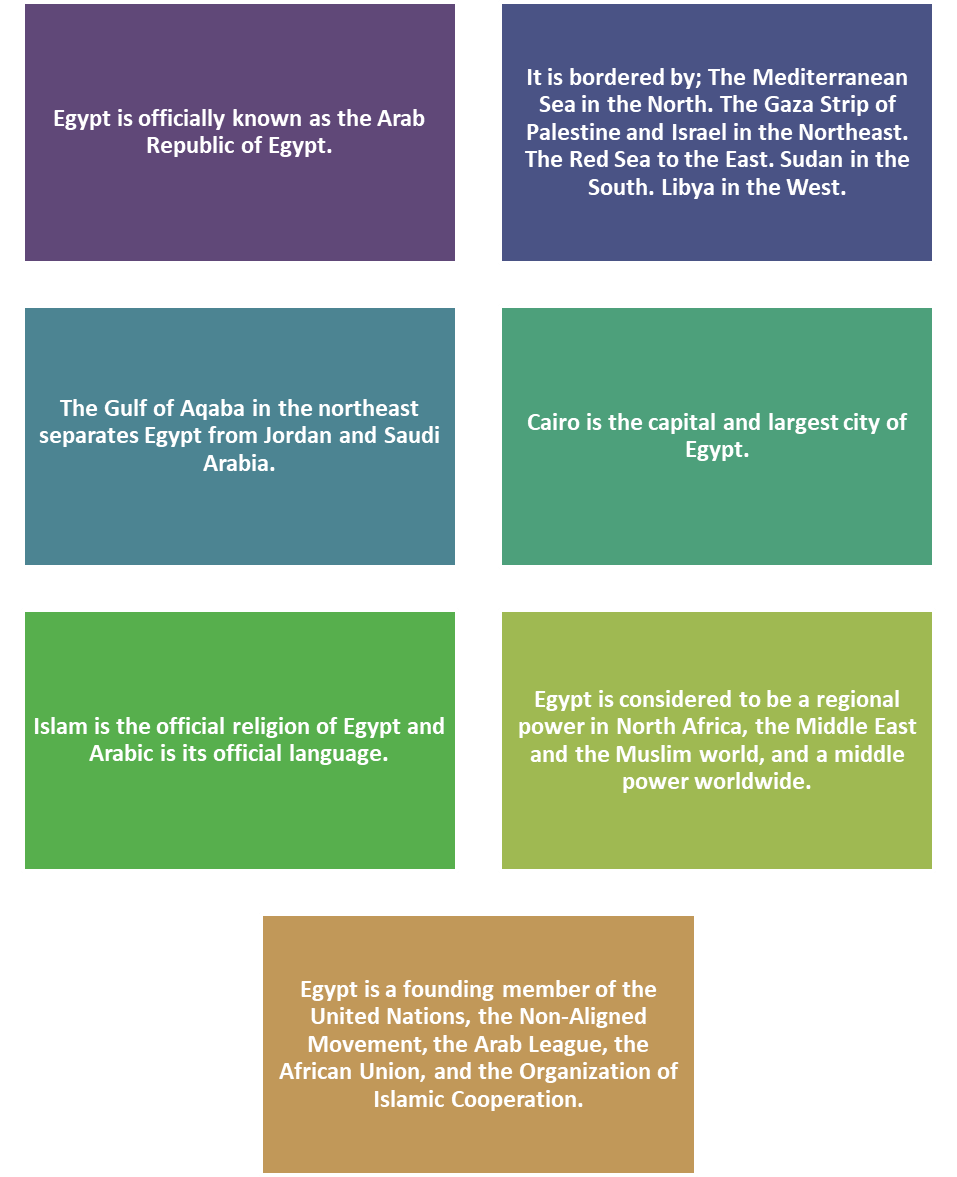
Egypt
To Download Monthly Current Affairs PDF Click here
Click here to get a free demo
Everything About CLAT 2025
Frequently Asked Questions
The “Great Pyramid of Giza” is located in which country?
The “Great Pyramid of Giza” is located in Egypt
Who decided to build the Great Pyramid of Giza?
Pharaoh Khufu decided to build the Great Pyramid of Giza
When was the Great Pyramid of Giza built?
The Great Pyramid of Giza was built in 2550 B.C.



