For strenghtning India-Africa relations, the 20-member Africa Expert Group (AEG), established by the Vivekananda International Foundation, recently presented the VIF Report entitled ‘India-Africa Partnership: Achievements, Challenges and Roadmap 2023’
Key Observations from the VIF Report on India-Africa Relations
- In the past 15 years and especially since 2014, India-Africa relations have developed steadily but more progress is achievable.
- The report examines the transitions unfolding in Africa: demographic, economic, political and social.
- It is slowly heading toward regional integration and is devoted to democracy, peace and progress, even as Ethiopia, Sudan, the Central African Republic and other countries continue to battle with the challenges posed by insurgency, ethnic violence and terrorism.
- External partners such as China, Russia, the United States, the European Union, Japan, Türkiye and the United Arab Emirates are trying to strengthen their relations with parts of Africa to ensure market access, gain energy and mineral security, and increase political and economic influence.
- China stands apart, armed with a consistent and robust policy since 2000 to become virtually Africa’s biggest economic partner.
- The VIF report notes that India has a substantive partnership with Africa and a rich fund of goodwill, but it is “essential for New Delhi to review its Africa policy periodically, stay resilient by making the required changes, and place a razor-like focus on its implementation”.
Recommendations For Strengthening India Africa Ties
- Political and diplomatic cooperation should be strengthened by restoring periodic leaders’ summits through the medium of the India-Africa Forum Summit
- A new annual strategic dialogue between the chairperson of the African Union (AU) and India’s External Affairs Minister should be launched in 2023.
- Seek consensus among G-20 members on the AU’s (African Union) full membership.
- The Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) should have a secretary exclusively in charge of African affairs to further enhance the implementation and impact of the Africa policy.
- Increase the number of defence attachés deployed in Africa, expand dialogue on defence issues, widen the footprint of maritime collaboration, and expand lines of credit to facilitate defence exports.
- Increase the number of defence training slots and enhance cooperation in counter-terrorism, cyber security and emerging technologies.
- Promote India-Africa trade through the creation of an Africa Growth Fund (AGF) to enhance access to finance.
- Socio-cultural cooperation should be increased through greater interaction between universities, think tanks, civil society and media organisations in India and select African countries.
- Setting up a National Centre for African Studies
- Visa measures for African students who come to India for higher education should be liberalised. They should also be given work visas for short periods.
- A special mechanism for implementing the ‘Roadmap 2030’.
India-Africa Relations
Historical Context of India-Africa Relations
- India and Africa have a long history of interaction, primarily through trade routes connecting the Indian Ocean region and the East African coast.
- Following the wave of decolonization in Africa during the mid-20th century, India played a significant role in supporting African nations’ struggles for independence.
- India’s own experience of colonial rule resonated with African nations, leading to the establishment of strong diplomatic and political ties.
- India’s leaders, such as Mahatma Gandhi and Jawaharlal Nehru, played a crucial role in fostering solidarity and cooperation between India and Africa.
- Both India and many African countries were founding members of the Non-Aligned Movement, which emerged during the Cold War era.
- NAM aimed to provide a platform for countries to maintain neutrality and pursue their own development agendas, free from the influence of major power blocs.
Economic and Trade Relations Between India and Africa
- India has been one of the major investors in Africa, with investments in sectors such as telecommunications, energy, infrastructure, agriculture, and manufacturing. Both sides aim to enhance bilateral trade and diversify their economic ties
- India-Africa trade touched $98 billion in FY22–23 which is a positive economic development.
Defence Cooperation: Strengthening India-Africa Security Ties
- India-Africa Defence Dialogue was held in the sidelines of DefExpo 2022 in Gandhinagar, Gujarat.
- Gandhinagar Declarationwas adopted to enhance cooperation in the fields of training & military exercises
Cultural relations
- The presence of the Indian diaspora in several African countries acts as a bridge between the two regions, facilitating cultural understanding, economic collaboration, and people-to-people connections
- Project ‘Mausam’is an initiative of Ministry of Culture which aims to explore the multi-faceted Indian Ocean ‘world’ and promote research on themes related to the study of maritime routes.
- About 39 Indian Ocean countries selected for this project which contains African countries like Egypt, Kenya, Sudan, Somalia etc.
Education and Health
- Africa is one of the beneficiaries of India’s flagship capacity building programme – Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC).
- India supplied ‘Made in India’ COVID vaccines to 42 African countries under “One Earth One Health Mission”.
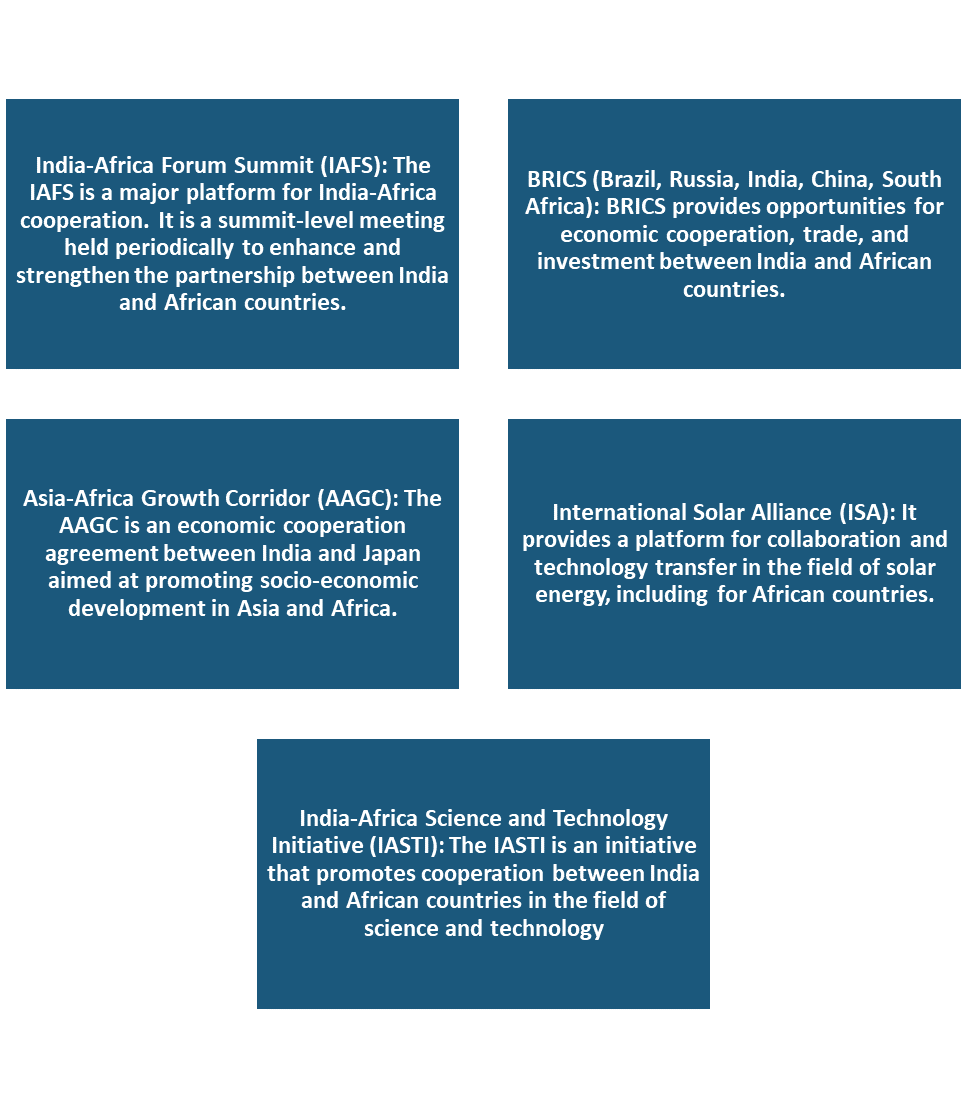
Regional Groupings and Forums for India-Africa Relations
To Download Monthly Current Affairs PDF Click here
Get Inspiration from CLAT 2025 Topper
Click here to get a free demo
Everything About CLAT 2025



