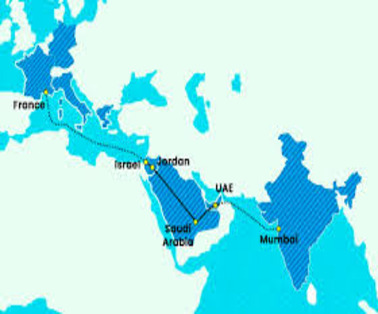
On the sidelines of the G20 Summit in New Delhi, a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was signed between the Governments of India, the US, Saudi Arabia, the European Union, the UAE, France, Germany and Italy to establish the India – Middle East – Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC).
What is IMEC?
- The India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEE-EC) is an infrastructure development project thataims to create connectivity through rail and shipping networks, energy cables, and data links.
- The IMEC aims to foster connectivity and economic integration between South Asia, Arabian Gulf and Europe.
- It is part of the Partnership for Rail and Shipping Corridors Global Infrastructure Investment (PGII) and focuses on enhancing global trade and cooperation through critical infrastructure development.
Key Features Of IMEC
- The India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) will be comprised of two separate corridors:
- The east corridor connecting India to the Arabian Gulf and
- The northern corridor connecting the Arabian Gulf to Europe
- A railway route will be a part of the arrangement, and once it is finished, it will offer a cross-border ship-to-rail transit network
- The movement of products and services to, from, and between India, the UAE, Saudi Arabia, Jordan, Israel, and Europe will be made possible by this.
- The members plan to install a cable for digital connectivity and energy together with a pipe for clean hydrogen export along the train track.
IMEC’s Strategic Significance
- This corridor will protect local supply chains, improve trade accessibility, and allow for a greater focus on the effects on the environment, society, and government.
- It will be created to boost economic cohesiveness, cut greenhouse gas emissions, create jobs, and increase efficiency, resulting in a dramatic integration of Asia, Europe, and the Middle East.
- It is an ambitious counter to China’s BRI project
- It also provides an opportunity to counter the growing Chinese geopolitical influence in the middle east
- This Corridor will help to bring countries in the Middle East together and establish that region as a hub for economic activity instead of as a “source of challenge, conflict or crisis” as it has been in recent history.
- It will reduced geopolitical dependence on Suez Canal and red sea
IMEC and The Partnership for Global Infrastructure Investment (PGII)
- The infrastructure plan was first announced in June 2021 during the G7 (or Group of Seven) summit in the UK.
- The G7 countries include the United Kingdom, the United States, Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, and the European Union (EU).
- US President Joe Biden had called it the Build Back Better World (B3W) framework. However, it did not register much progress.
- In 2022, during the G7 summit in Germany, the PGII was officially launched as a joint initiative to help fund infrastructure projects in developing countries through public and private investments.
- Essentially, in response to the infrastructure projects being undertaken and funded by China under the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) at a global level, the G7 decided to present their alternative mechanism for it.
- The stated purpose of both the PGII and the BRI is to help secure funding for countries to build critical infrastructure such as roads, ports, bridges, communication setups, etc. to enhance global trade and cooperation.
What Has Been Announced So Far As Part Of PGII Initiatives?
- The PGII announced clean energy projects in Indonesia to support sustainable energy sources and infrastructure development.
- The US government’s agency, its International Development Finance Corporation (DFC) would invest over $15 million in India’s health infrastructure
- The EU, through its Global Gateway programme, has now said it will “activate 300 billion of investments in critical connectivity projects during the period 2021-2027, half of which is destined for Africa.”
- Trans-African Corridor will connect the port of Lobito in Angola with Katanga province in Congo and the copper belt in Zambia
Key Benefits of IMEC for India
- Enhancing food security, regional supply chains, trade accessibility, environmental considerations, economic cohesion, job creation, and reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
- Reliable cross-border ship-to-rail transit network connecting India, the UAE, Saudi Arabia, Jordan, Israel, and Europe.
- It offers India a crucial role in global commerce, digital communication, and energy networks vis-à-vis China’s BRI
- It firmly positions India along the trade route spanning South East Asia to the Gulf, West Asia, and Europe
To Download Monthly Current Affairs PDF Click here
Click here to get a free demo
Everything About CLAT 2025