Nineteen countries expressed an interest in joining the BRICS group of nations as it prepares to hold an annual summit in South Africa.
Key Points On BRICS
- The emerging-markets bloc of Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa will meet in Cape Town on June 2-3 to discuss its enlargement
- Thirteen countries have formally asked to join and another six have asked informally
- China initiated the conversation about expansion, as the world’s second-biggest economy tries to build diplomatic clout to counter the dominance of developed countries in the United Nations.
- The proposed enlargement triggered concern among other members that their influence will be diluted, especially if Beijing’s close allies are admitted.
- China’s gross domestic product is more than twice the size of all four other members combined.
- Since its formation as the BRIC, the group has only added one new member — South Africa in 2010.
- Saudi Arabia and Iran are among the countries who’ve formally asked to join
- Other countries that have expressed interest in joining include Argentina, the United Arab Emirates, Algeria, Egypt, Bahrain and Indonesia, along with two nations from East Africa and one from West Africa
Evolution Of BRICS
- It is an acronym for the grouping of the world’s leading emerging economies, namely Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa.
- In 2001, the British Economist Jim O’Neill coined the term BRIC to describe the four emerging economies of Brazil, Russia, India, and China
- The grouping was formalised during the first meeting of BRIC Foreign Ministers’ in 2006.
- It has met every year and set up several initiatives
- It may be disparate countries on four continents, but they together representing 41% of the global population, 24% of the global GDP and 16% of the global trade.
BRICS Background
- Unlike other regional, economic and political groupings, the idea came not from its members, but from a paper by a Goldman Sachs economist in 2001
- In those days, Russia had just been taken into the G-7 to make it the G-8, but it was still an outlier.
- In 2009, the leaders of the four countries met and formed BRIC, adding South Africa in 2010. Russia’s ties with the West had begun to unravel after the war with Georgia in 2008, and Russia was ousted from G-7 by 2014.
What Are The Practical BRICS Initiatives
New Development Bank or BRICS bank
During the Sixth BRICS Summit in Fortaleza (Brazil) in 2014, the leaders signed the Agreement establishing the New Development Bank (NDB – Shanghai, China). It has so far approved 70 infrastructure and sustainable development projects worth $ 25.07 billion. The Bank is headquartered in Shanghai, China
Contingent Reserve Arrangement
In 2014, the BRICS governments had signed a treaty on the setting up of the contingent reserve arrangement. The arrangement is aimed at forestalling short-term balance of payments pressures, provide mutual support and strengthen financial stability of the BRICS nations.
BRICS payment system
It is an alternative to the SWIFT payment system. This has taken on a new urgency as post Ukraine war, Russia has been frozen out of SWIFT.
Customs agreement to coordinate and ease trade transport between countries
A Remote Sensing constellation of satellites has been launched – with 6 satellites including 2 from India, 2 from China, 1 from Russia, and 1 Brazil-China collaboration
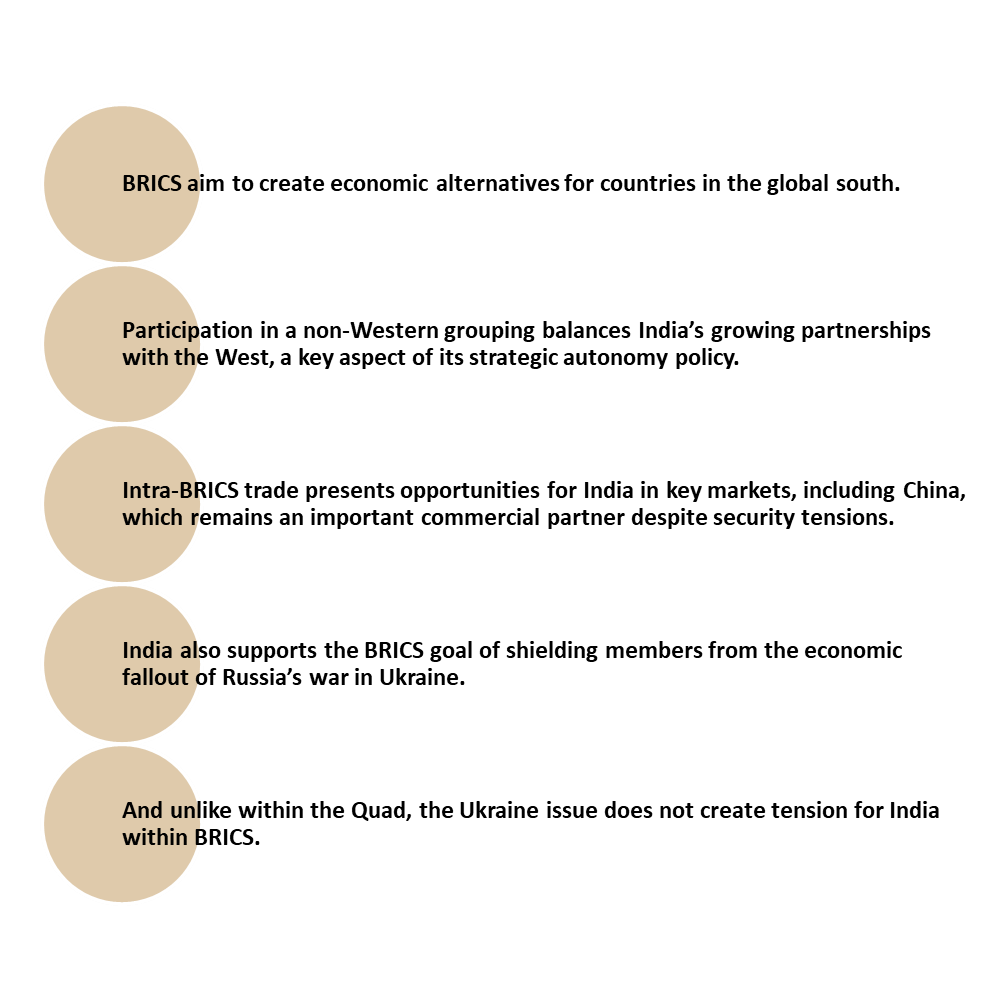
How Important Is BRICS To India?
Criticism Of BRICS
- It has long been questioned and even mocked for being an unworkable idea
- The grouping countries never kept the promise of developing economies– and still only make up about a quarter of the global GDP.
- Russia, Brazil, South Africa economies have frequently been on the verge of collapse, the Indian economy has been disappointing, particularly in the past decade
- China, which was in touching distance of the US, has been dealt a big blow by Covid and the lockdowns that have followed.
- The members don’t discuss bilateral issues, but issues like the India-China border dispute and PLA transgressions over the LAC are bound to have an impact on BRICS solidarity in the long run
- India and even Russia are not part of China’s big infrastructure push the Belt and Road Initiative, while Brazil and South Africa are
- The BRICS document emphasizing National Positions on Ukraine, indicates there are differences between the members over Russia’s actions, and this could prove problematic in the years ahead.
- While China and Russia have come closer, especially with the announcement of a no-limits partnership, India, Brazil and South Africa have all made outreaches to the US and Europe in equal if not greater measure
To Download Monthly Current Affairs PDF Click here
Get Inspiration from CLAT 2025 Topper
Click here to get a free demo
Everything About CLAT 2025
Frequently Asked Questions
Which country joined the BRICS in 2010?
South Africa joined the BRICS in 2010
The acronym BRICS was initially formulated in 2001 by?
The acronym BRICS was initially formulated in 2001 by Jim O’Neill
BRICS payment system is an alternative to which system?
BRICS payment system is an alternative to SWIFT payment system



