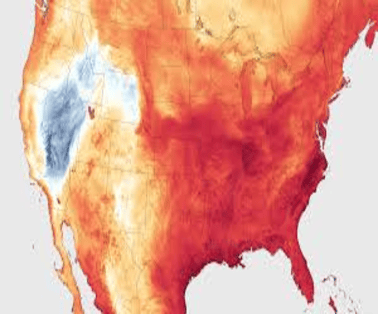
In July 2023, Death Valley in Southern California recorded one of the world’s highest temperatures ever at a scorching 53.3°C. This extreme temperature was part of a larger, global weather phenomenon as other regions in the US also faced the effects of a heat dome.
Key Points
- Other parts of the US, too, faced a heat dome — a concentrated heat sphere that descended over most of the Southern US — raising temperatures to the extremes.
- Aside from that, the US faced tumultuous weather conditions, including 19 severe storms, 1 tropical storm, and 2 flooding events that led to the death of almost 500 people.
- Each of these events caused damages worth a billion dollars, according to US government data.
- The summer of 2023 saw scorching heat waves across northern and peninsular India.
- According to the IMD, several cities in Bihar, Uttar Pradesh and Rajasthan recorded temperatures over 44°C in April and May.
- At least 99 people died in UP and Bihar together, and the number is said to be more but there is no accurate data available.
- A report by World Weather Attribution showed that human-induced climate change made the 2023 heatwaves 2°C warmer than usual, and that the frequency of these events would increase with increased global warming.
What Is A Heat Dome?
- A heat dome occurs when an area of high-pressure traps warm air over a region, just like a lid on a pot, for an extended period of time.
- The longer that air remains trapped, the more the sun works to heat the air, producing warmer conditions with every passing day.
- Heat domes generally stay for a few days but sometimes they can extend up to weeks, which might cause deadly heat waves.
- Scientists suggest that any region of high pressure, whether a heat dome or not, forces air to sink and once it reaches the ground, it gets compressed and becomes even warmer.
- Moreover, when air sinks, it gets drier and further raises the temperature of the area.
Heat Domes And The Jet Stream
- The heat dome’s formation is related to the behaviour of the jet stream — an area of fast-moving air high in the atmosphere.
- The jet stream is believed to have a wave-like pattern that keeps moving from north to south and then north again.
- When these waves get bigger and elongated, they move slowly and sometimes can become stationary.
- This is when a high-pressure system gets stuck and leads to the occurrence of a heat dome.
- Although heat domes are likely to have always existed, researchers say that climate change may be making them more intense and longer.
- They suggest with the rising temperatures, it is expected that the jet stream will become more wavy and will have larger deviations, causing more frequent extreme heat events.
Some Previous Instances Of Heat Domes
- In 2021, a heat dome formed over western Canada and the US, causing deadly heat waves.
- Portland city in Oregon, US, saw the mercury rise to 46 degree Celsius while the temperature in Washington hit 49 degree Celsius.
- In Lytton in British Columbia, temperatures soared to over 46 degree Celsius.
- According to media reports, hundreds of people are believed to have died due to this extreme weather event.
- Subsequently, a 2022 study found that this heat dome was amplified by climate change and it could become a once-in-10-year event if global temperatures aren’t kept under two degree Celsius above pre-industrialisation levels.
- The researchers said that the dry soil — one of the repercussions of the rising temperatures — in different areas of the Pacific northwest “potentially allowed the heat to become more extreme, and so they amplified the heat that was already at a high level”.
- Another heat dome settled over the US in September 2022 and raised temperatures to a new high. The extreme heat fueled wildfires and stressed the power grid.
Impact of Heat Domes
- Those living without an air conditioner see the temperatures of their homes rising to unbearably high, leading to sudden fatalities.
- The trapping of heat can also damage crops, dry out vegetation and result in droughts.
- The sweltering heat wave will also lead to rise in energy demand, especially electricity, leading to pushing up rates.
- The heat domes can also act as fuel to wildfires, which destroys a lot of land area in the US every year.
To Download Monthly Current Affairs PDF Click here
Click here to get a free demo
Everything About CLAT 2026